
During touch, mechanoreceptors in the skin and other tissues respond to variations in pressure. During smell, olfactory receptors recognize molecular features of wafting odors.
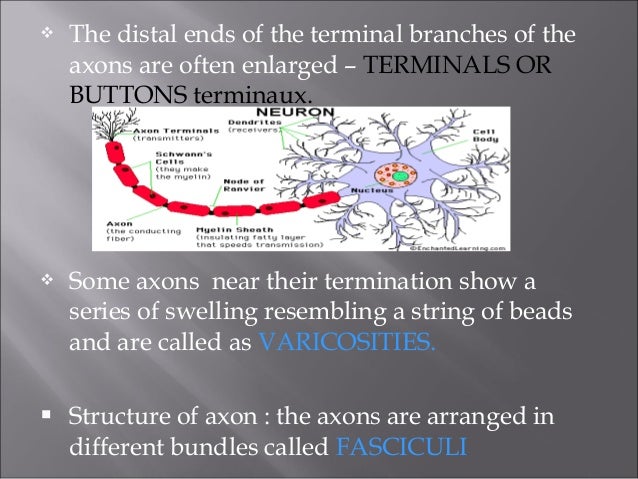
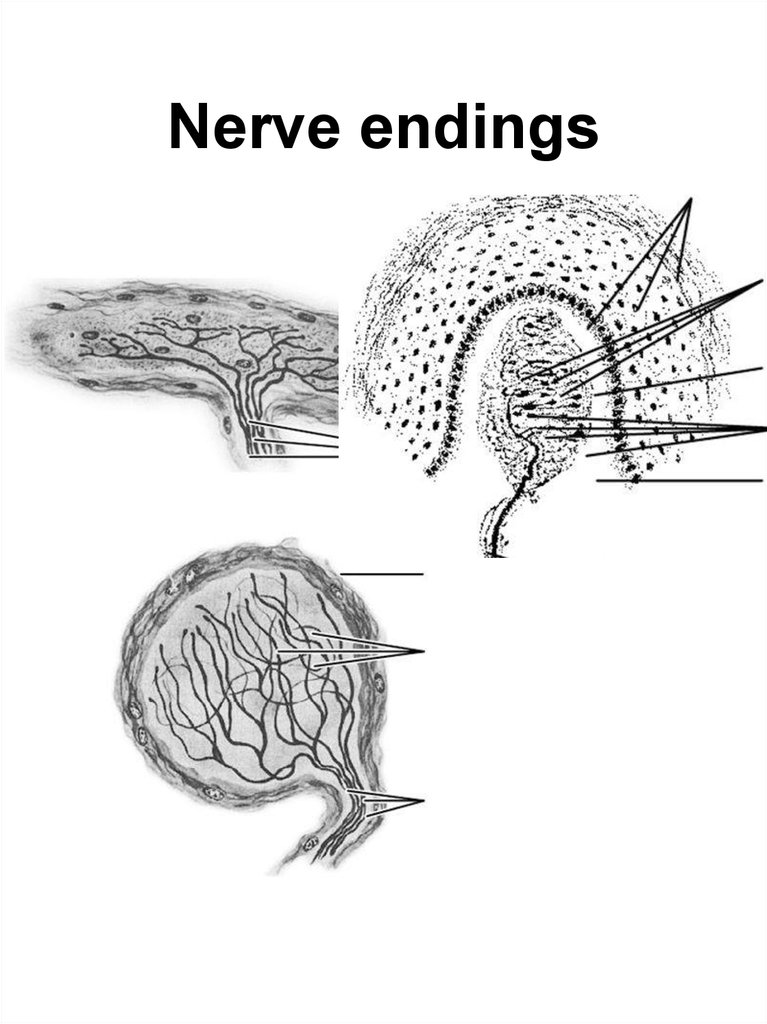
Free nerve endings and encapsulated free#
During taste, sensory neurons in our taste buds detect chemical qualities of our foods including sweetness, bitterness, sourness, saltiness, and umami (savory taste). Free nerve ending receptors - separate spots on skin are sensitive to hot or to cold. Free nerve endings are sensitive to painful stimuli, to hot and cold, and to light touch. A free nerve ending is an unencapsulated dendrite of a sensory neuron they are the most common nerve endings in skin. Schematization of an encapsulated nerve ending as compared to a free nerve ending. Mechanoreceptors in the skin are described as encapsulated or unencapsulated. Ruffini endings, Pacinian corpuscles, and free nerve endings are most prevalent in the fibrous joint capsule Golgi tendon organs are most common in the. Free nerve endings are the most abundant type of nerve endings. Mechanoreceptors are primary neurons or nerve endings that respond to. During hearing, mechanoreceptors in hair cells of the inner ear detect vibrations conducted from the eardrum. The first three types are encapsulated the fourth is unencapsulated: type I, Ruffini endings type II, Pacinian corpuscles type III, Golgi tendon organs and type IV, free nerve endings. During vision, rod and cone photoreceptors respond to light intensity and color. Sensory receptors perform countless functions in our bodies. free nerve ending synonyms, free nerve ending pronunciation, free nerve ending translation, English dictionary definition of free nerve ending.
For example, hygroreceptors that respond to changes in humidity and osmoreceptors that respond to the osmolarity of fluids may do so via a mechanosensory mechanism or may detect a chemical characteristic of the environment. In some cases, the mechanism of action for a receptor is not clear. Function as light touch receptors - Free nerve endings, Hair follicle receptors, Tactile corpuscles b. Broadly, sensory receptors respond to one of four primary stimuli:Ī schematic of the classes of sensory receptors: Sensory receptor cells differ in terms of morphology, location, and stimulus.Īll sensory receptors rely on one of these four capacities to detect changes in the environment, but may be tuned to detect specific characteristics of each to perform a specific sensory function. Sensory receptors can be classified by the type of stimulus that generates a response in the receptor. these neurons travel through the Cranial or Spinal nerves to the brain or spinal cord. baroreceptor: A nerve ending that is sensitive to changes in blood pressure.mechanoreceptor: Any receptor that provides an organism with information about mechanical changes in its environment such as movement, tension, and pressure.photoreceptor: A specialized neuron able to detect and react to light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
